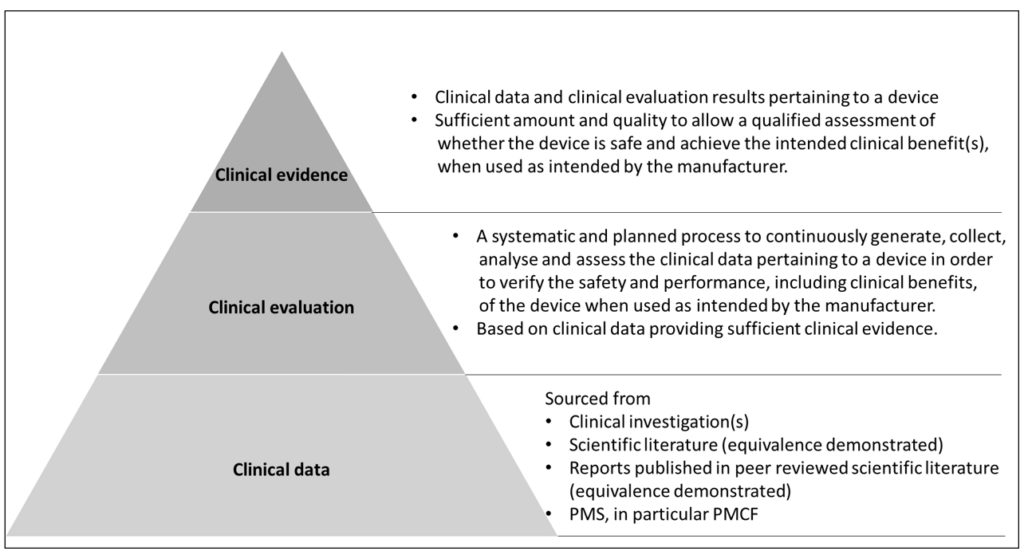
Relationship of clinical data, clinical evaluation and clinical evidence
欧洲 欧盟医疗器械法规 (MDR) defines Clinical evaluation as a systematic and planned process to continuously generate, collect, analyse and assess the clinical data pertaining to a device in order to verify the safety and performance, including clinical benefits, of the device when used as intended by the manufacturer.
Compared to the MDD/AIMDD, the EU MDR raises the bar significantly by requiring sound clinical evidence in conformity assessment and post-market surveillance of a medical device. It is therefore, a key to deep dive into these clinical requirements and under the difference and link between clinical data, clinical evaluation and clinical evidence.
The following Figure shows a pyramidal relationship between the concepts of clinical data, clinical evaluation and clinical evidence. Here, clinical data is a pool of data derived from clinical investigations, scientific literature, reports published in peer-reviewed scientific literature and PMS, especially PMCF. The manufacturer analyses and assesses these clinical data pertaining to a device to verify the safety and performance, including clinical benefits, of the device when used as intended. Based on the clinical data and the results of clinical evaluation, the manufacturer shall demonstrate that there are sufficient amount and quality of clinical data to allow a qualified assessment of the safety and clinical benefit of the device when used as intended, which is referred to as “clinical evidence”.
Clinical evaluation process
Although the new MDR and MDD/AIMDD have much in common in terms of the process for conducting clinical evaluation, there are definitely differences between directives and regulation. Please find more detail in another blog.
Clinical evaluation is initiated in the early phase of the device design to identify the gaps between available clinical data and the required clinical data, and to analyse the available clinical data to determine whether the clinical evidence is sufficient to declare compliance with the appropriate GSPRs (general safety and performance requirements) as required by the EU MDR. The overall clinical evaluation process includes the following steps, shown in the following Figure. This process is an iterative process through the life cycle of the medical device.

Through the process of clinical evaluation, the manufacturer should consider the following:
1) Clinical evaluation is a series of the planned activities; in this context, the manufacturer must plan clinical evaluation in advance and document the clinical evaluation in the Clinical Evaluation Plan (CEP), as specified in Part A of Annex XIV of the MDR.
2) Manufacturer must review all available data sources to identify the clinical data. The strategy for identifying the data should be documented in the CEP.
3) Use methodologically sound methods to analyse and assess data. The rationale for selecting either qualitative or quantitative method, or a combination of both, should be documented in the CEP. The outcome of this process should be documented in the Clinical Evaluation Report (CER).
4) Verify the safety and performance of the medical devices and confirm clinical benefit for demonstration of compliance with the relevant GSPRs when the device is used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction for use; if the gap is identified, i.e. compliance with the GSPRs cannot be demonstrated, the manufacturer must generate clinical data by either conducting clinical investigation or expanding the scope of the ongoing clinical evaluation. The result of this process is clinical evaluation report, which documents the clinical evidence and is an element of the technical documentation.
5) The clinical evaluation is not a one-time activity, but should be performed continuously throughout the life cycle of the device. Whenever a change in the product design or manufacturing process has an impact on the safety and performance of the device, the clinical evaluation must be updated.
6) The clinical evaluation must be performed by qualified personnel or a team with expertise in research methodology, information management, regulatory requirements, device technology, diagnosis and management of the conditions to be treated, as specified in Section 6.4 of MEDDEV 2.7/1 rev. 4.
7) Clinical data and clinical evaluation results on a device in sufficient quantity and quality to allow a qualified evaluation to demonstrate conformance with the general safety and performance requirements, which includes clinical benefit to patients.
